Examination of Mustard Flower, Gram Seed and Maize Grain
Abstract
This practical explores the structural features of Mustard flower, Gram seed, and Maize grain using a hand lens or microscope. It helps understand plant reproductive and storage systems by comparing monocots and dicots.
Introduction
Plant structures like flowers and seeds play vital roles in reproduction. Mustard is a complete flower, Gram is a dicot seed, and Maize is a monocot grain. Observing them develops an understanding of key botanical differences.
Procedure
- Collect a Mustard flower, Gram seed, and Maize grain.
- Use a hand lens or dissecting microscope for observation.
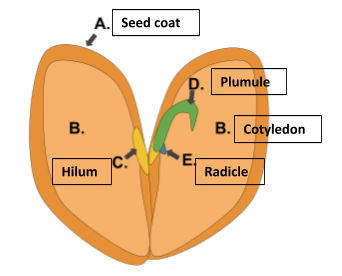
- Remove the seed coat of Gram to expose its cotyledons.
- Slice the Maize grain to view its single cotyledon and endosperm.
- Draw labeled diagrams of all three specimens.
Observation and Diagrams
- Mustard Flower: A complete flower with sepals, petals, stamens, and pistil.
- Gram Seed: Dicot with two cotyledons, seed coat, and visible embryo.
- Maize Grain: Monocot with a single cotyledon, endosperm, and embryo.

20 Short Questions with Answers
- What type of flower is Mustard? It is a complete, bisexual flower.
- What is a dicotyledon? A seed with two cotyledons.
- How many cotyledons does Maize have? One cotyledon.
- Which part contains pollen? The anther of the stamen.
- Function of petals? Attract pollinators using color and scent.
- What covers Gram seed? A seed coat (testa).
- What is the endosperm? Food-storing tissue for the embryo.
- Is Gram seed monocot or dicot? Dicot.
- What does the embryo develop into? A complete plant.
- Reproductive parts of Mustard? Stamens and pistil/carpel.
- Role of cotyledons? Supply stored food to embryo.
- Which seed has more endosperm? Maize grain.
- Role of sepals? Protect the flower bud.
- Is maize a seed or fruit? It is a fruit (caryopsis).
- Which seed splits in half? Gram seed.
- Unique feature of monocot seed? Single cotyledon, large endosperm.
- What is a complete flower? Has sepals, petals, stamens, and pistil.
- Function of ovary in Mustard? Contains ovules; forms fruit.
- Which part forms seed? Ovule.
- Difference in seed coat? Gram has thick coat; Maize has thin fused coat.
5 Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
- How many cotyledons does a Gram seed have?
Ⓐ One Ⓑ Two Ⓒ None Ⓓ Four
Answer: Ⓑ Two - Which part of the flower contains ovules?
Ⓐ Petals Ⓑ Sepals Ⓒ Ovary Ⓓ Anthers
Answer: Ⓒ Ovary - What is the function of endosperm in Maize grain?
Ⓐ Photosynthesis Ⓑ Reproduction Ⓒ Storage of food Ⓓ Protection
Answer: Ⓒ Storage of food - Mustard flower is:
Ⓐ Incomplete Ⓑ Complete Ⓒ Monocot Ⓓ Asexual
Answer: Ⓑ Complete - Which one of the following is a monocot seed?
Ⓐ Gram Ⓑ Mustard Ⓒ Maize Ⓓ Bean
Answer: Ⓒ Maize
Tags
Biology Practical
Class 10 Biology
FBISE Practicals
Federal Board Pakistan
Gram Seed
Maize Grain
Monocot vs Dicot
Mustard Flower
Practical Exam Guide
SSC-II Biology





